Python Coroutines 파이썬 코루틴
Python 2023. 9. 11. 12:58 |반응형
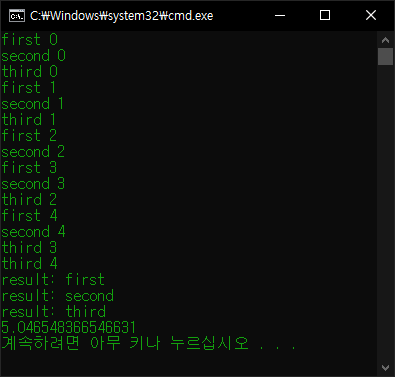
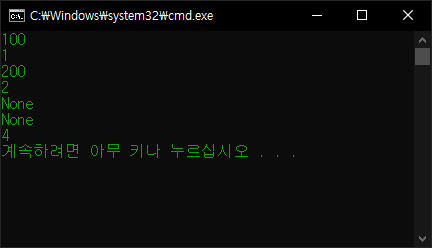
코루틴과 데이터를 교환해서 처리해 보자.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
import time
def MyCoroutine():
num = 0
while True:
x = yield num
num += 1
print(x)
time.sleep(0.5)
co = MyCoroutine()
next(co)
time.sleep(1)
# 코루틴을 시작하고 yield 명령에서 대기한다.
print(co.send(100))
time.sleep(1)
# 코루틴에 100을 전달(x에 100 대입)하고 num을 받아서 출력한다.
# num 값은 yield 명령이 실행되는 시점에 결정된 값(0)이 아니고
# 코루틴이 끝나는 시점에 결정된 값(1)이 전달된다.
print(co.send(200))
time.sleep(1)
# 코루틴에 200을 전달(x에 200 대입)하고 num을 받아서 출력한다.
next(co)
# 코루틴에 아무 값도 전달하지 않고(그래서 None이 출력된다) 다음
# yield 까지 진행하고 받아온 num 값은 무시.
print(next(co))
# 마찬가지로 코루틴에 아무 값도 전달하지 않고 다름 yield 까지 진행.
# 이번엔 num 값을 받아서 출력한다.
co.close()
|
반응형
'Python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Pygame] PyOpenGL 파이게임 (0) | 2023.09.11 |
|---|---|
| Python PyOpenGL (0) | 2023.09.11 |
| Python Coroutines and Tasks 파이썬 코루틴과 태스크 (0) | 2023.09.11 |
| Python Multi Thread Class 파이썬 멀티 스레드 클래스 (0) | 2023.09.10 |
| Python Multi Thread 파이썬 멀티 스레드 (0) | 2023.09.10 |