[SDL3] SDL3 with Dear ImGui (Image rendering)
SDL, raylib 2025. 4. 12. 22:37 |SDL3에 Dear ImGui를 사용해 보자. 아래 링크를 참고해 SDL3를 준비한다.
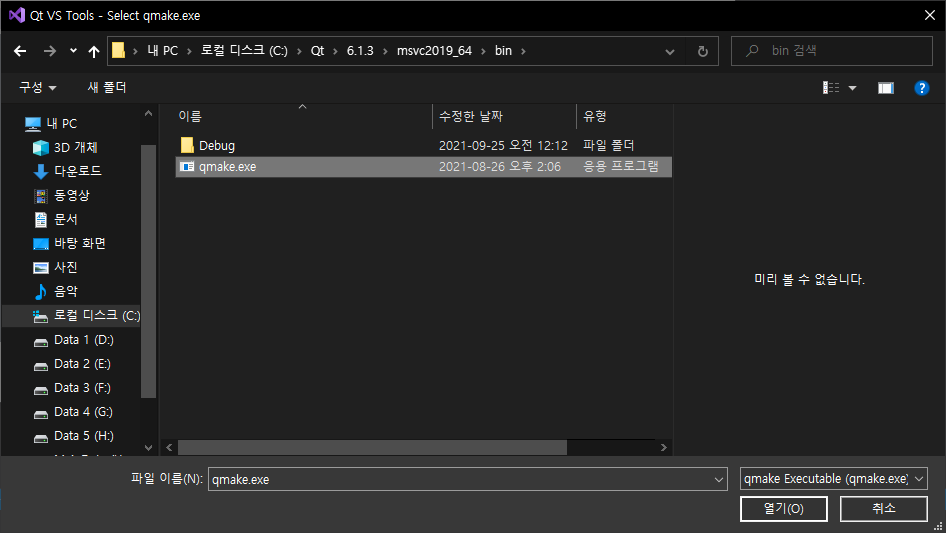
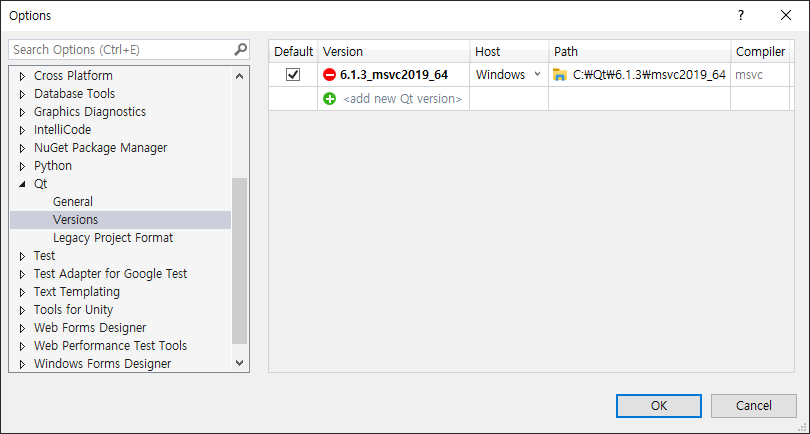
2025.03.30 - [C, C++] - [SDL3] Simple DirectMedia Layer 3 Setup and Getting Started - SDL3 설정 및 초기화


|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
|
#define SDL_MAIN_USE_CALLBACKS 1
#include <SDL3/SDL.h>
#include <SDL3/SDL_main.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <Windows.h>
#include "imgui.h"
#include "imgui_impl_sdl3.h"
#include "imgui_impl_sdlrenderer3.h"
static SDL_Window* window = NULL;
static SDL_Renderer* renderer = NULL;
ImGuiIO* pio = NULL;
SDL_AppResult SDL_AppInit(void** appstate, int argc, char* argv[])
{
SDL_SetAppMetadata("Example Renderer Clear", "1.0", "com.example.renderer-clear");
if (!SDL_Init(SDL_INIT_VIDEO)) {
SDL_Log("Couldn't initialize SDL: %s", SDL_GetError());
return SDL_APP_FAILURE;
}
if (!SDL_CreateWindowAndRenderer("examples/renderer/clear", 640, 480, 0, &window, &renderer)) {
SDL_Log("Couldn't create window/renderer: %s", SDL_GetError());
return SDL_APP_FAILURE;
}
// Setup Dear ImGui context
IMGUI_CHECKVERSION();
ImGui::CreateContext();
ImGuiIO& io = ImGui::GetIO(); (void)io;
// (void)io는 의미 없는 명령. just to avoid compiler warning on unused variable
pio = &io;
// io가 SDL_AppIterate()에서 사용되기 때문에 전역 포인터 변수 pio에 대입.
io.ConfigFlags |= ImGuiConfigFlags_NavEnableKeyboard; // Enable Keyboard Controls
//io.ConfigFlags |= ImGuiConfigFlags_NavEnableGamepad; // Enable Gamepad Controls
// Setup Dear ImGui style
//ImGui::StyleColorsDark();
ImGui::StyleColorsLight();
// Setup Platform/Renderer backends
ImGui_ImplSDL3_InitForSDLRenderer(window, renderer);
ImGui_ImplSDLRenderer3_Init(renderer);
return SDL_APP_CONTINUE;
}
SDL_AppResult SDL_AppEvent(void* appstate, SDL_Event* event)
{
// Poll and handle events (inputs, window resize, etc.)
// You can read the io.WantCaptureMouse, io.WantCaptureKeyboard flags to tell if dear imgui wants to use your inputs.
// - When io.WantCaptureMouse is true, do not dispatch mouse input data to your main application, or clear/overwrite your copy of the mouse data.
// - When io.WantCaptureKeyboard is true, do not dispatch keyboard input data to your main application, or clear/overwrite your copy of the keyboard data.
// Generally you may always pass all inputs to dear imgui, and hide them from your application based on those two flags.
ImGui_ImplSDL3_ProcessEvent(event);
switch (event->type) {
case SDL_EVENT_QUIT:
return SDL_APP_SUCCESS;
case SDL_EVENT_KEY_DOWN:
printf("Key pressed: %s\n", SDL_GetKeyName(event->key.key));
if (event->key.key == SDLK_ESCAPE)
return SDL_APP_SUCCESS;
break;
default:
break;
}
return SDL_APP_CONTINUE;
}
SDL_AppResult SDL_AppIterate(void* appstate)
{
// Start the Dear ImGui frame
ImGui_ImplSDLRenderer3_NewFrame();
ImGui_ImplSDL3_NewFrame();
ImGui::NewFrame();
// Show a simple window that we create ourselves. We use a Begin/End pair to create a named window.
{
static float f = 0.0f;
static int counter = 0;
ImGui::Begin("Hello, world!"); // Create a window called "Hello, world!" and append into it.
//ImGui::SetWindowSize(ImVec2(100, 20)); // 매 프레임마다 윈도우 사이즈를 (100, 20)으로 지정한다.
//ImGui::SetWindowSize(ImVec2(100, 20), ImGuiCond_Once); // 프로그램을 시작할때 한 번만 윈도우 사이즈를 지정한다.
//ImGui::SetWindowSize(ImVec2(100, 20), ImGuiCond_FirstUseEver); // 프로그램을 처음 시작할때(imgui.ini파일이 존재하지 않을때)
// 한 번만 윈도우 사이즈를 지정한다.
ImGui::Text("This is some useful text."); // Display some text (you can use a format strings too)
if (ImGui::Button("Button")) // Buttons return true when clicked (most widgets return true when edited/activated)
counter++;
ImGui::SameLine();
ImGui::Text("counter = %d", counter);
ImGui::Text("Application average %.3f ms/frame (%.1f FPS)", 1000.0f / pio->Framerate, pio->Framerate);
ImGui::End();
}
// 윈도우 없이 위치가 고정된 버튼 생성하기.
{
ImGui::Begin("No Window", 0, ImGuiWindowFlags_NoBackground | ImGuiWindowFlags_NoDecoration);
ImGui::SetWindowPos(ImVec2(10, 20));
ImGui::SetWindowSize(ImVec2(100, 20));
// WindowSize()는 이 예제 블럭에서 생성하려는 버튼의 사이즈를 지정하는 함수가 아니다. 버튼을 포함하는 윈도우의 사이즈다.
// 이 예제는 윈도우가 보이지 않으므로 사이즈를 지정하지 않으면 버튼 사이즈보다 훨씬 크게 지정되서 근처의 다른 UI가
// 이 윈도우에 가려져 제대로 동작하지 않을 수 있다. (보이기는 하지만 클릭이 되지 않는다)
// 아니면, Begin()에서 ImGuiWindowFlags_NoBringToFrontOnFocus 옵션을 추가하면 다른 윈도우의 UI 동작을 방해하지 않는다.
// 이 예제에서 ImGuiWindowFlags_NoInputs 옵션은 버튼을 비활성화 시키므로 사용하면 안된다.
ImGui::Button("Fixed Button");
ImGui::End();
}
// Rendering
ImGui::Render();
SDL_SetRenderDrawColor(renderer, 255, 255, 255, SDL_ALPHA_OPAQUE);
SDL_RenderClear(renderer);
ImGui_ImplSDLRenderer3_RenderDrawData(ImGui::GetDrawData(), renderer);
SDL_RenderPresent(renderer);
return SDL_APP_CONTINUE;
}
void SDL_AppQuit(void* appstate, SDL_AppResult result)
{
// Cleanup
ImGui_ImplSDLRenderer3_Shutdown();
ImGui_ImplSDL3_Shutdown();
ImGui::DestroyContext();
SDL_DestroyRenderer(renderer);
SDL_DestroyWindow(window);
SDL_Quit();
}
|
소스를 입력하고 빌드한다.

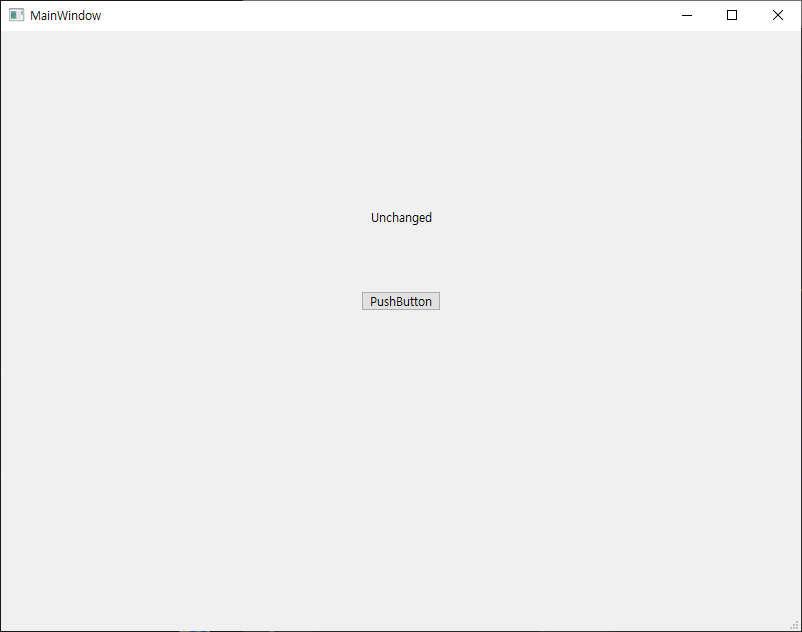
이번엔 ImGui를 이용해 이미지를 출력해 보자.

Image Loading and Displaying Examples
위 링크를 참고해 소스를 작성한다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
|
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#define STB_IMAGE_IMPLEMENTATION
#define SDL_MAIN_USE_CALLBACKS 1
#include <SDL3/SDL.h>
#include <SDL3/SDL_main.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <Windows.h>
#include "imgui.h"
#include "imgui_impl_sdl3.h"
#include "imgui_impl_sdlrenderer3.h"
#include "stb_image.h"
static SDL_Window* window = NULL;
static SDL_Renderer* renderer = NULL;
ImGuiIO* pio = NULL;
SDL_Texture* my_texture;
int my_image_width, my_image_height;
bool LoadTextureFromMemory(const void* data, size_t data_size, SDL_Renderer* renderer, SDL_Texture** out_texture, int* out_width, int* out_height)
{
int image_width = 0;
int image_height = 0;
int channels = 4;
unsigned char* image_data = stbi_load_from_memory((const unsigned char*)data, (int)data_size, &image_width, &image_height, NULL, 4);
if (image_data == nullptr)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to load image: %s\n", stbi_failure_reason());
return false;
}
SDL_Surface* surface = SDL_CreateSurfaceFrom(image_width, image_height, SDL_PIXELFORMAT_RGBA32, (void*)image_data, channels * image_width);
if (surface == nullptr)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to create SDL surface: %s\n", SDL_GetError());
return false;
}
SDL_Texture* texture = SDL_CreateTextureFromSurface(renderer, surface);
if (texture == nullptr)
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to create SDL texture: %s\n", SDL_GetError());
*out_texture = texture;
*out_width = image_width;
*out_height = image_height;
SDL_DestroySurface(surface);
stbi_image_free(image_data);
return true;
}
// Open and read a file, then forward to LoadTextureFromMemory()
bool LoadTextureFromFile(const char* file_name, SDL_Renderer* renderer, SDL_Texture** out_texture, int* out_width, int* out_height)
{
FILE* f = fopen(file_name, "rb");
if (f == NULL)
return false;
fseek(f, 0, SEEK_END);
size_t file_size = (size_t)ftell(f);
if (file_size == -1)
return false;
fseek(f, 0, SEEK_SET);
void* file_data = IM_ALLOC(file_size);
fread(file_data, 1, file_size, f);
fclose(f);
bool ret = LoadTextureFromMemory(file_data, file_size, renderer, out_texture, out_width, out_height);
IM_FREE(file_data);
return ret;
}
SDL_AppResult SDL_AppInit(void** appstate, int argc, char* argv[])
{
SDL_SetAppMetadata("Example Renderer Clear", "1.0", "com.example.renderer-clear");
if (!SDL_Init(SDL_INIT_VIDEO)) {
SDL_Log("Couldn't initialize SDL: %s", SDL_GetError());
return SDL_APP_FAILURE;
}
if (!SDL_CreateWindowAndRenderer("examples/renderer/clear", 640, 480, 0, &window, &renderer)) {
SDL_Log("Couldn't create window/renderer: %s", SDL_GetError());
return SDL_APP_FAILURE;
}
// Setup Dear ImGui context
IMGUI_CHECKVERSION();
ImGui::CreateContext();
ImGuiIO& io = ImGui::GetIO(); (void)io;
// (void)io는 의미 없는 명령. just to avoid compiler warning on unused variable
pio = &io;
// io가 SDL_AppIterate()에서 사용되기 때문에 전역 포인터 변수 pio에 대입.
io.ConfigFlags |= ImGuiConfigFlags_NavEnableKeyboard; // Enable Keyboard Controls
//io.ConfigFlags |= ImGuiConfigFlags_NavEnableGamepad; // Enable Gamepad Controls
// Setup Dear ImGui style
//ImGui::StyleColorsDark();
ImGui::StyleColorsLight();
// Setup Platform/Renderer backends
ImGui_ImplSDL3_InitForSDLRenderer(window, renderer);
ImGui_ImplSDLRenderer3_Init(renderer);
// Load our texture after initialising SDL
bool ret = LoadTextureFromFile("palvin.jpg", renderer, &my_texture, &my_image_width, &my_image_height);
IM_ASSERT(ret);
return SDL_APP_CONTINUE;
}
SDL_AppResult SDL_AppEvent(void* appstate, SDL_Event* event)
{
// Poll and handle events (inputs, window resize, etc.)
// You can read the io.WantCaptureMouse, io.WantCaptureKeyboard flags to tell if dear imgui wants to use your inputs.
// - When io.WantCaptureMouse is true, do not dispatch mouse input data to your main application, or clear/overwrite your copy of the mouse data.
// - When io.WantCaptureKeyboard is true, do not dispatch keyboard input data to your main application, or clear/overwrite your copy of the keyboard data.
// Generally you may always pass all inputs to dear imgui, and hide them from your application based on those two flags.
ImGui_ImplSDL3_ProcessEvent(event);
switch (event->type) {
case SDL_EVENT_QUIT:
return SDL_APP_SUCCESS;
case SDL_EVENT_KEY_DOWN:
printf("Key pressed: %s\n", SDL_GetKeyName(event->key.key));
if (event->key.key == SDLK_ESCAPE)
return SDL_APP_SUCCESS;
break;
default:
break;
}
return SDL_APP_CONTINUE;
}
SDL_AppResult SDL_AppIterate(void* appstate)
{
// Start the Dear ImGui frame
ImGui_ImplSDLRenderer3_NewFrame();
ImGui_ImplSDL3_NewFrame();
ImGui::NewFrame();
// Show a simple window that we create ourselves. We use a Begin/End pair to create a named window.
{
static float f = 0.0f;
static int counter = 0;
ImGui::Begin("Hello, world!"); // Create a window called "Hello, world!" and append into it.
ImGui::Text("This is some useful text."); // Display some text (you can use a format strings too)
if (ImGui::Button("Button")) // Buttons return true when clicked (most widgets return true when edited/activated)
counter++;
ImGui::SameLine();
ImGui::Text("counter = %d", counter);
ImGui::Text("Application average %.3f ms/frame (%.1f FPS)", 1000.0f / pio->Framerate, pio->Framerate);
ImGui::End();
}
// 윈도우 없이 위치가 고정된 이미지 생성하기.
{
ImGui::Begin("No Window", 0, ImGuiWindowFlags_NoBackground | ImGuiWindowFlags_NoDecoration | ImGuiWindowFlags_NoBringToFrontOnFocus | ImGuiWindowFlags_NoInputs);
ImGui::SetWindowPos(ImVec2(0, 0));
ImGui::Text("pointer = %p", my_texture);
ImGui::Text("size = %d x %d", my_image_width, my_image_height);
ImGui::Image((ImTextureID)(intptr_t)my_texture, ImVec2((float)my_image_width, (float)my_image_height));
ImGui::End();
}
// Rendering
ImGui::Render();
SDL_SetRenderDrawColor(renderer, 255, 255, 255, SDL_ALPHA_OPAQUE);
SDL_RenderClear(renderer);
ImGui_ImplSDLRenderer3_RenderDrawData(ImGui::GetDrawData(), renderer);
SDL_RenderPresent(renderer);
return SDL_APP_CONTINUE;
}
void SDL_AppQuit(void* appstate, SDL_AppResult result)
{
// Cleanup
ImGui_ImplSDLRenderer3_Shutdown();
ImGui_ImplSDL3_Shutdown();
ImGui::DestroyContext();
SDL_DestroyRenderer(renderer);
SDL_DestroyWindow(window);
SDL_Quit();
}
|

'SDL, raylib' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [SDL3] Particle 파티클 (Fireworks/Snow) (0) | 2025.04.18 |
|---|---|
| [SDL3] SDL3 Popup Window (0) | 2025.04.13 |
| [SDL3] Simple DirectMedia Layer 3 Setup and Getting Started - SDL3 설정 및 초기화 (1) | 2025.03.30 |
| [SDL] SDL 2D Camera - 2D 카메라 (0) | 2024.02.01 |
| [SDL] SDL Box2D Collision Contact Point & Normal Vector - Box2D 충돌 지점과 법선 벡터 (0) | 2024.01.31 |