방송통신대학교(방송대/방통대) Sorting Algorithms in Python 파이썬 정렬 알고리즘 2
General 2024. 3. 22. 15:14 |반응형
기본 정렬 알고리즘 세 가지(퀵, 머지, 힙)를 파이게임(Pygame)으로 시각화 해 보자.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
|
import os
import random
os.environ['PYGAME_HIDE_SUPPORT_PROMPT'] = '1'
import pygame
from math import ceil, floor
pygame.init()
pygame.display.set_caption("Sorting Visualization")
screensize = (640, 580)
screen = pygame.display.set_mode(screensize)
clock = pygame.time.Clock()
framerate = 10
running = True
font = pygame.font.Font(None, 30)
text = font.render("Sorting Visualization\n\n" +
"*q: Quick Sorting [ O(nlogn) ]\n" +
"*m: Merge Sorting [ O(nlogn) ]\n" +
"*h: Heap Sorting [ O(nlogn) ]\n" +
"\n*g: Random Data Generation", True, "gray")
text_pos = text.get_rect()
text_pos.center = (screen.get_width()/2, text_pos.height/2)
data_size = 64
data = list()
data_color = list()
def DataGenerator():
global data
global data_color
data = [random.randint(10, 400) for i in range(data_size)]
data_color = [(random.randint(0, 255), random.randint(0, 255), random.randint(0, 255))
for i in range(data_size)]
DataGenerator()
def Visualize():
screen.fill("black")
screen.blit(text, text_pos)
for i in range(data_size):
pygame.draw.rect(screen, data_color[i], (i*10, screensize[1]-data[i], 10, data[i]))
pygame.display.flip()
clock.tick(framerate)
def Finalize():
screen.fill("white")
pygame.display.flip()
clock.tick(framerate)
def EventHandler():
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN and event.key == pygame.K_ESCAPE:
return -1
elif event.type == pygame.QUIT:
exit()
def QuickSort(start, end):
if start >= end:
return
pivot = start
left = start + 1
right = end
while left <= right:
if EventHandler() == -1:
return
while left <= end and data[left] <= data[pivot]:
left += 1
while right > start and data[right] >= data[pivot]:
right -= 1
if left > right:
data[right], data[pivot] = data[pivot], data[right]
data_color[right], data_color[pivot] = data_color[pivot], data_color[right]
else:
data[left], data[right] = data[right], data[left]
data_color[left], data_color[right] = data_color[right], data_color[left]
Visualize()
QuickSort(start, right-1)
QuickSort(right+1, end)
def MergeSort_1(data_list, color_list):
if len(data_list) < 2:
return data_list, color_list
mid = len(data_list) // 2
low_data_list, low_color_list = MergeSort_1(data_list[:mid], color_list[:mid])
high_data_list, high_color_list = MergeSort_1(data_list[mid:], color_list[mid:])
merged_data_list = list()
merged_color_list = list()
l = h = 0
while l < len(low_data_list) and h < len(high_data_list):
if low_data_list[l] < high_data_list[h]:
merged_data_list.append(low_data_list[l])
merged_color_list.append(low_color_list[l])
l += 1
else:
merged_data_list.append(high_data_list[h])
merged_color_list.append(high_color_list[h])
h += 1
merged_data_list += low_data_list[l:]
merged_color_list += low_color_list[l:]
merged_data_list += high_data_list[h:]
merged_color_list += high_color_list[h:]
return merged_data_list, merged_color_list
def MergeSort_2():
def sort(low, high):
if EventHandler() == -1:
return
if high - low < 2:
return
mid = (low + high) // 2
sort(low, mid)
sort(mid, high)
merge(low, mid, high)
def merge(low, mid, high):
data_temp = list()
color_temp = list()
l, h = low, mid
while l < mid and h < high:
if data[l] < data[h]:
data_temp.append(data[l])
color_temp.append(data_color[l])
l += 1
else:
data_temp.append(data[h])
color_temp.append(data_color[h])
h += 1
while l < mid:
data_temp.append(data[l])
color_temp.append(data_color[l])
l += 1
while h < high:
data_temp.append(data[h])
color_temp.append(data_color[h])
h += 1
for i in range(low, high):
data[i] = data_temp[i - low]
data_color[i] = color_temp[i - low]
Visualize()
sort(0, data_size)
def HeapSort():
for i in range(len(data)):
par = ceil(i/2) - 1
while par >= 0 and data[par] < data[i]:
data[par], data[i] = data[i], data[par]
data_color[par], data_color[i] = data_color[i], data_color[par]
i = par
par = floor((i-1)/2)
for i in range(len(data)-1, 0, -1):
data[0], data[i] = data[i], data[0]
data_color[0], data_color[i] = data_color[i], data_color[0]
cur = 0
lch = 1
rch = 2
while True:
if EventHandler() == -1:
return
if rch < i and data[lch] < data[rch]:
lch = rch
if lch < i and data[lch] > data[cur]:
data[lch], data[cur] = data[cur], data[lch]
data_color[lch], data_color[cur] = data_color[cur], data_color[lch]
Visualize()
cur = lch
lch = cur * 2 + 1
rch = cur * 2 + 2
else:
lch = i # break와 같은 효과
if not lch < i:
break
while running:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
running = False
elif event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN and event.key == pygame.K_ESCAPE:
running = False
elif event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN and event.key == pygame.K_q:
QuickSort(0, data_size - 1)
Finalize()
elif event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN and event.key == pygame.K_m:
MergeSort_2()
Finalize()
elif event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN and event.key == pygame.K_n:
data, data_color = MergeSort_1(data, data_color)
Finalize()
elif event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN and event.key == pygame.K_h:
HeapSort()
Finalize()
elif event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN and event.key == pygame.K_g:
DataGenerator()
Visualize()
|
코드를 작성하고 실행한다.
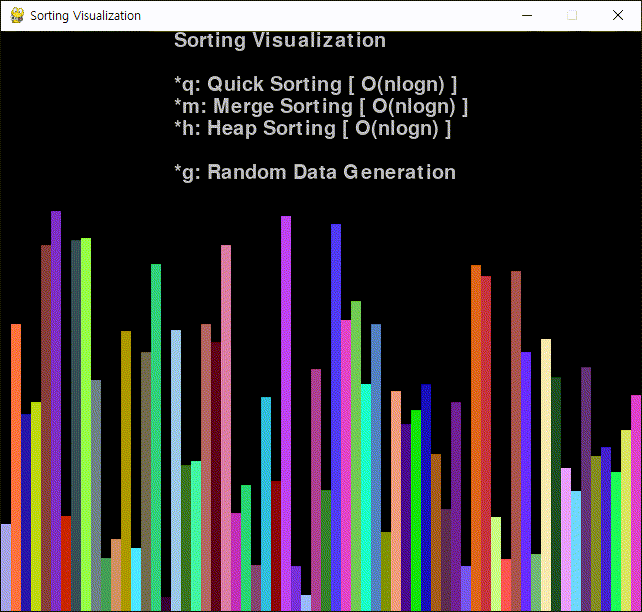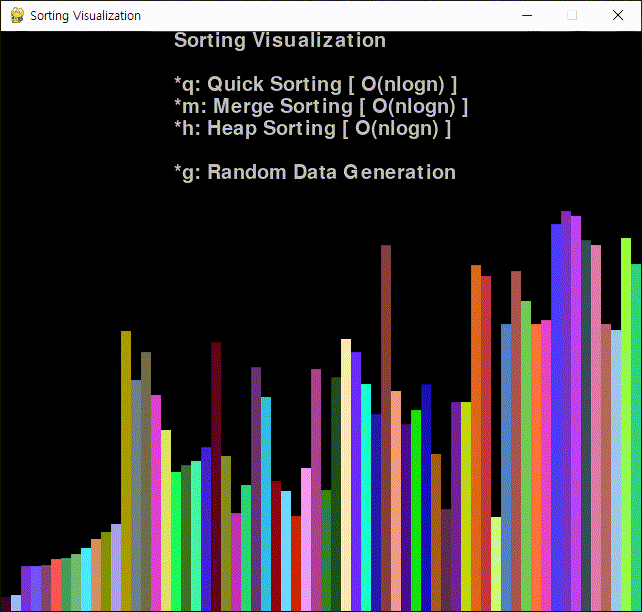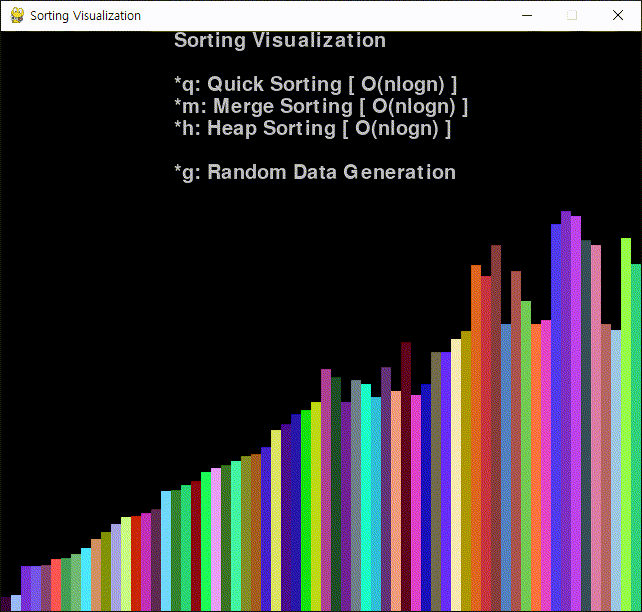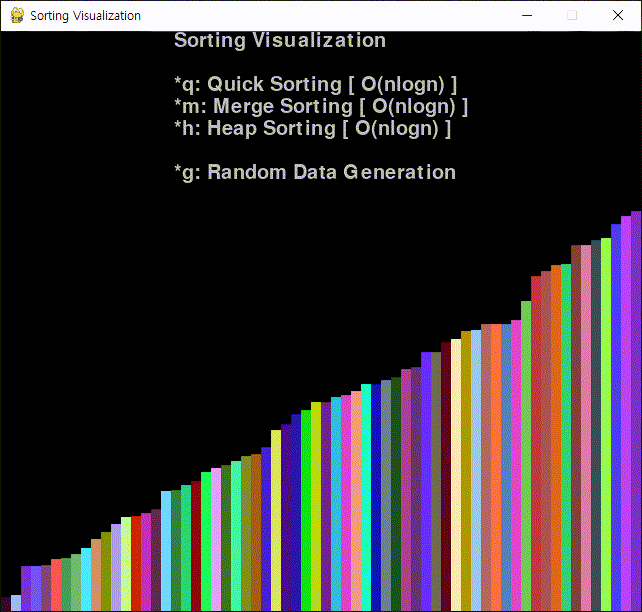
※ 참고
2024.03.09 - [Python] - [Pygame] Sorting Algorithms in Python 파이썬 정렬 알고리즘 1
알고리즘_05_강의록.pdf
3.91MB
알고리즘_04_강의록.pdf
1.86MB
반응형
'General' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Visual Studio] Debugging Breakpoint 디버깅 브레이크 포인트 활용 (0) | 2025.05.28 |
|---|---|
| PDF 파일 프린트 속도가 너무 느릴 때 해결 방법 (1) | 2024.10.28 |
| 방송통신대학교(방송대/방통대) Sorting Algorithms in Python 파이썬 정렬 알고리즘 1 (1) | 2024.03.09 |
| GIMP Alpha Channel Transparent Layer/Background 투명 배경 (0) | 2024.02.20 |
| Pixel(JPG/PNG) Image To Vector(AI) Image 픽셀 이미지를 벡터 이미지로 변환하기 (0) | 2023.12.17 |

