Raspberry Pi Pico & RP2040-Zero - 라즈베리 파이 피코
Raspberry Pi & Arduino 2021. 11. 18. 17:55 |

Raspberry Pi Pico를 사용해 보자.


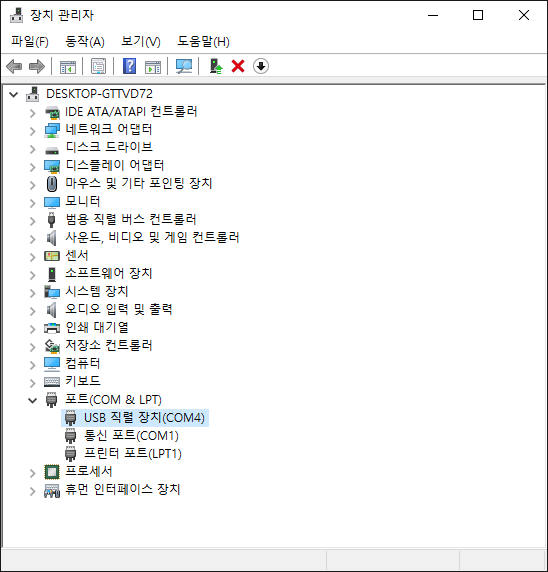
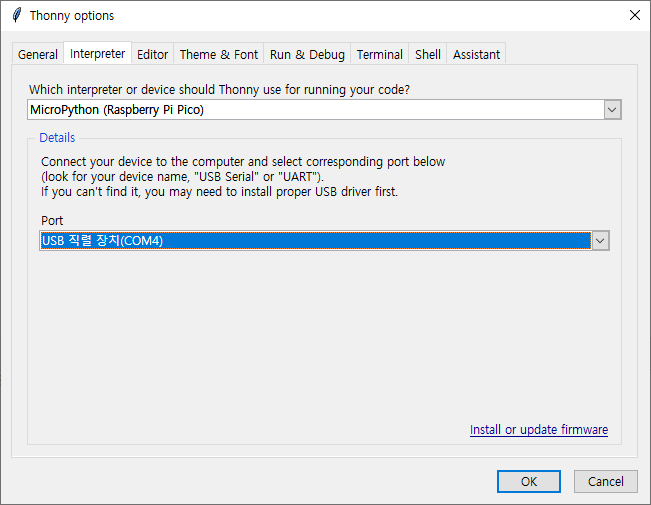
만약 파일 익스플로러에 Pico가 표시되지 않는다면 BOOTSEL 버튼을 누른 상태에서 컴퓨터에 연결한다.

MicroPython is a full implementation of the Python 3 programming language that runs directly on embedded hardware like Raspberry Pi Pico. You get an interactive prompt (the REPL) to execute commands immediately via USB Serial, and a built-in filesystem. The Pico port of MicroPython includes modules for accessing low-level chip-specific hardware.


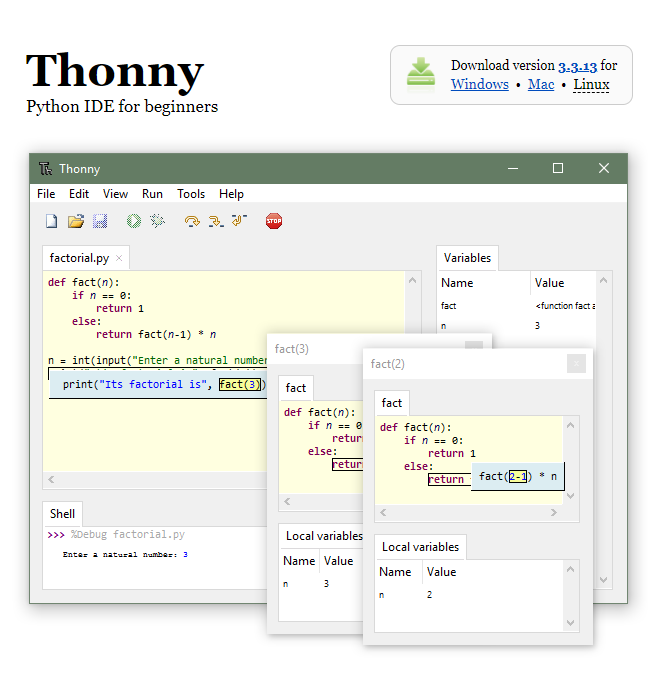

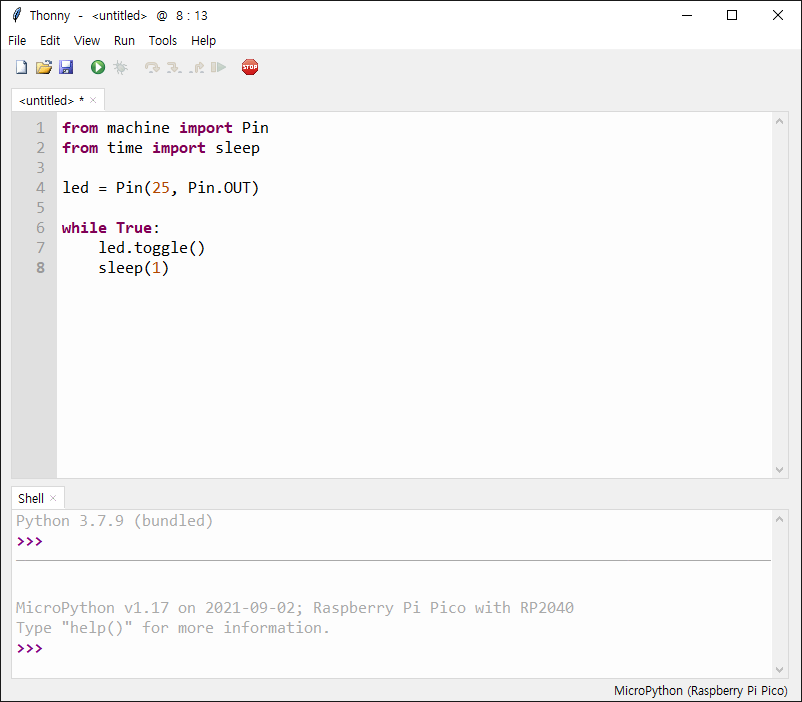


Run 버튼을 클릭했으므로 소스가 저장되고 나면 바로 실행된다.
Pico에 달려있는 LED(GP25)가 1초 간격으로 깜빡인다.




RP2040-Zero는 Raspberry Pi Pico와 Pinout이 다르고 단색 LED가 아닌 WS2812 RGB LED(GP16)가 사용되었다.
단색 LED가 아니기 때문에 간단한 Blink.py 예제는 동작하지 않는다.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
|
import time
from machine import Pin
import rp2
max_lum =100
r=0
g=0
b=0
@rp2.asm_pio(sideset_init=rp2.PIO.OUT_LOW, out_shiftdir=rp2.PIO.SHIFT_LEFT, autopull=True, pull_thresh=24)
def ws2812():
T1 = 2
T2 = 5
T3 = 3
wrap_target()
label("bitloop")
out(x, 1) .side(0) [T3 - 1]
jmp(not_x, "do_zero") .side(1) [T1 - 1]
jmp("bitloop") .side(1) [T2 - 1]
label("do_zero")
nop() .side(0) [T2 - 1]
wrap()
# Create the StateMachine with the ws2812 program, outputting on Pin(4).
sm = rp2.StateMachine(0, ws2812, freq=8_000_000, sideset_base=Pin(16))
# Start the StateMachine, it will wait for data on its FIFO.
sm.active(1)
# Color change
while True:
for i in range(0,max_lum):
r=i
b=max_lum-i
rgb =(g<<24) | (r<<16) | (b<<8)
sm.put(rgb)
time.sleep_ms(10)
time.sleep_ms(300)
for i in range(0,max_lum):
g=i
r=max_lum-i
rgb =(g<<24) | (r<<16) | (b<<8)
sm.put(rgb)
time.sleep_ms(10)
time.sleep_ms(300)
for i in range(0,max_lum):
b=i
g=max_lum-i
rgb =(g<<24) | (r<<16) | (b<<8)
sm.put(rgb)
time.sleep_ms(10)
time.sleep_ms(300)
|
조금 복잡한 WS2812 Test Code로 RGB값 변화를 확인할 수 있다.

